A growing focus on responding to mass casualty events by hospitals and emergency response agencies across the country has placed Dr. Alexander Eastman at the forefront of policy discussions and preparedness efforts. With a unique blend of trauma surgery, law enforcement experience, and operational management, Dr. Eastman’s career has positioned him to contribute to discussions on improving immediate trauma care before reaching the operating room.
His work combines aspects of clinical medicine, public safety operations, and national preparedness programs; therefore, it was natural that he would be involved in the Hartford Consensus. The Hartford Consensus is an initiative aimed at reducing preventable deaths in active shooter and mass casualty situations, which reflects the multiple themes found throughout Dr. Eastman’s career. The following news article reviews how Dr. Eastman became involved in the Hartford Consensus, the experience he brought to the effort, and how his work continues to influence preparedness strategies nationwide.
Preparation Through Career to Position Himself as National Preparedness Leader
Dr. Eastman developed much of his career path while working at Parkland Memorial Hospital in Dallas, Texas. Parkland is nationally recognized as a leading trauma center for its ability to manage large volumes of critically injured patients. Through his work at Parkland, Dr. Eastman developed extensive experience treating a wide range of injuries and complex resuscitative conditions. Additionally, Dr. Eastman received training in both surgical critical care and emergency medical services (EMS), enabling him to understand the complexities of trauma systems and the operational challenges that arise at each level of care.
Perhaps more importantly than the education or the environment of Dr. Eastman’s career was the decision to become a police officer. While a member of the Dallas Police Department, Dr. Eastman served in both tactical and medical leadership positions. These experiences provided Dr. Eastman with a direct understanding of how injuries occur in the field, how first responders deliver early care, and where gaps exist between on-scene care and hospital-based interventions.
This unique combination of Dr. Eastman’s trauma experience, critical care training, and front-line law enforcement experience gave Dr. Eastman a very unique dual perspective. This experience formed the basis for Dr. Eastman’s participation in future national preparedness initiatives.
Involvement With the Hartford Consensus Meetings
When experts met to discuss active shooter and mass casualty incidents, Dr. Eastman had already completed numerous research projects and presentations concerning hemorrhage control, tactical medical support, and pre-hospital trauma care. Dr. Eastman had also conducted studies examining law enforcement injury patterns, early bleeding control, and coordinated responses among first responding agencies.
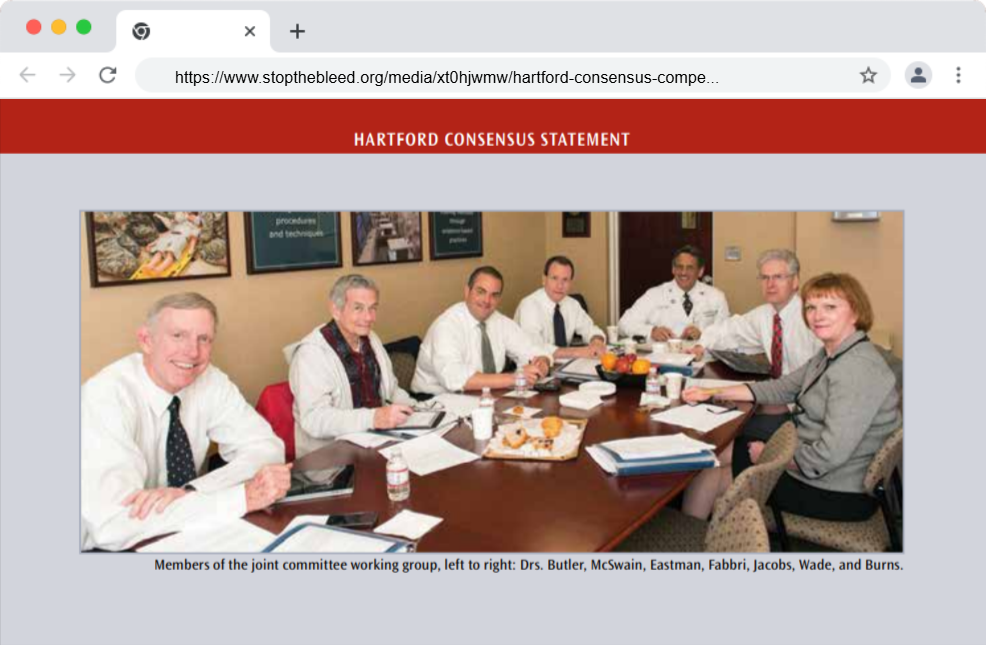
Due to these experiences, Dr. Alexander Eastman was one of the few professionals who combined both clinical and field expertise to help meet the objectives of the Hartford Consensus. Dr. Eastman’s input to the Hartford Consensus meetings drew upon firsthand experience from trauma centers and operational environments.
At the beginning of the meetings, Dr. Eastman offered insight regarding two primary themes of the Hartford Consensus: the importance of early bleeding control and the need for improved communication and coordination between law enforcement and medical providers. Both areas are based on Dr. Eastman’s own experience working in Dallas.
Evolution of Dr. Eastman’s Involvement With the Hartford Consensus
As the Hartford Consensus generated subsequent reports and recommendations, Dr. Eastman remained actively engaged. Dr. Eastman’s involvement included providing oral presentations at national conferences, briefings to public safety officials, and presentations of the Hartford Consensus recommendations to clinicians, policymakers, and emergency response agencies.

Throughout the evolution of the Hartford Consensus, Dr. Eastman maintained his other professional responsibilities. Dr. Eastman practiced clinically, supported tactical operations, taught in academia, and assumed leadership roles in operational medicine and emergency preparedness. These other professional responsibilities provided Dr. Eastman with opportunities to implement the Hartford Consensus recommendations in real-world settings and to utilize the practical knowledge acquired to contribute to national discussions.
Increasing Focus on Hemorrhage Control and Public Awareness
Nationwide, one of the most obvious shifts resulting from the Hartford Consensus was the increased focus on immediate bleeding control. The Hartford Consensus recommendation that civilians receive education and training in basic hemorrhage control led to a rapid increase in public training programs teaching hemorrhage control techniques. In addition, the Hartford Consensus helped establish the Stop the Bleed initiative.
Dr. Alexander Eastman has participated in educational efforts on hemorrhage control and continues to advocate for the importance of rapid intervention to stop bleeding at the point of injury. Dr. Eastman’s work helped to increase awareness of the impact that early intervention can have on survivability in traumatic events. Dr. Eastman’s work also helped shape changes in how organizations purchase and distribute medical equipment, including tourniquets and bleeding-control kits.
Continued Influence on National Preparedness
Dr. Alexander Eastman currently serves in federal operational medicine and homeland security programs. In these capacities, Dr. Eastman uses lessons learned from years of trauma care and law enforcement experience to inform national-level planning and preparation for disaster response.
The Hartford Consensus will always represent a pivotal moment in Dr. Eastman’s career. The Hartford Consensus represented the intersection of his clinical, tactical, and operational leadership at a time when there was a need for national guidance on developing effective strategies to respond to mass casualty events. Dr. Eastman’s involvement in the Hartford Consensus helped shape the recommendations that many agencies continue to use today to prepare for and respond to mass casualty events.

